The Importance of a Healthy Diet in Maintaining Well-being
A healthy diet is crucial for maintaining optimal physical and mental health. It provides the body with essential nutrients, helps in weight management, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases. A balanced diet ensures that you consume adequate amounts of vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, proteins, and fats necessary for your body’s functioning.
Simple Guidelines for a Balanced Diet
Portion Control
Portion control is vital in managing your calorie intake and preventing overeating. Eating too much can lead to weight gain and related health issues. Understanding how much food your body needs and being mindful of serving sizes can help you maintain a healthy weight. For example, a serving of meat should be about the size of a deck of cards, while a serving of rice or pasta is approximately one cup.
Nutrient-Dense Food Choices
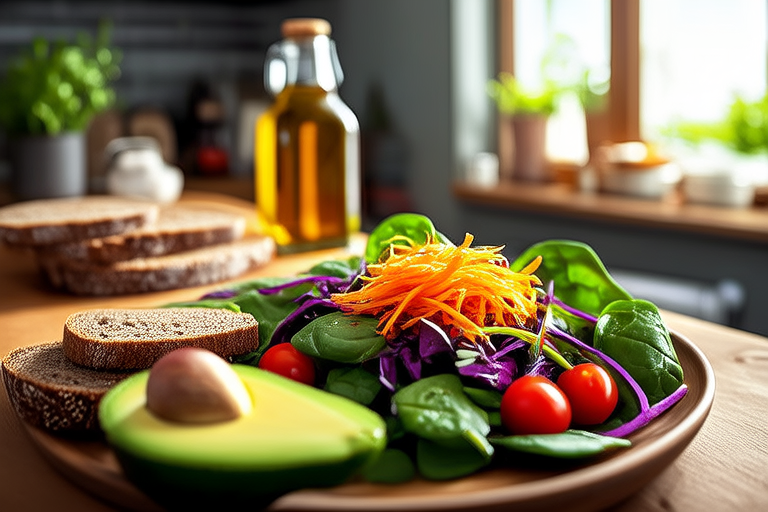
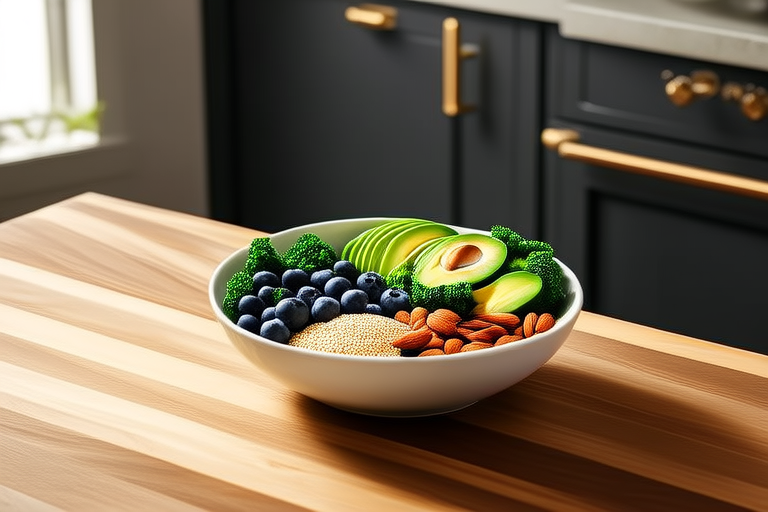
Selecting nutrient-dense foods means choosing items that provide substantial amounts of vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial substances with relatively few calories. These foods include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Nutrient-dense foods support overall health, enhance energy levels, and improve mood.
Hydration
Drinking enough water throughout the day is essential for digestion, circulation, temperature regulation, and waste removal. Water also helps transport nutrients to cells, lubricate joints, and protect organs and tissues. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water daily, but individual needs may vary depending on activity level, climate, and health conditions.
The Role of Macronutrients
Carbohydrates: Carbs are the primary source of energy for the body. They come in two forms: simple and complex. Simple carbs, like sugar, are quickly digested and can cause spikes in blood sugar levels. Complex carbs, such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, take longer to digest and provide sustained energy. Aim for complex carbs in your diet.
Proteins: Proteins are vital for building and repairing tissues, making enzymes and hormones, and supporting immune function. Protein sources include lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, beans, lentils, nuts, and seeds. Incorporating a variety of protein sources ensures you get all the essential amino acids your body needs.
Fats: Fats play a crucial role in hormone production, cell membrane structure, and absorbing fat-soluble vitamins. However, not all fats are created equal. Saturated and trans fats found in processed foods, fried foods, and animal products can increase cholesterol levels and contribute to heart disease. On the other hand, unsaturated fats from avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish promote heart health and reduce inflammation.
Incorporating Whole Grains, Lean Proteins, Healthy Fats, Fruits, and Vegetables
Whole Grains: Whole grains are rich in fiber, B vitamins, and minerals. They provide sustained energy and help regulate blood sugar levels. Examples of whole grains include brown rice, quinoa, oats, barley, and whole wheat bread. Incorporating whole grains into your meals can improve digestive health and lower the risk of heart disease.
Lean Proteins: Lean proteins are low in saturated fat and high in essential amino acids. They support muscle growth, repair, and maintenance. Good sources of lean protein include skinless chicken breast, turkey, fish, tofu, legumes, and low-fat dairy products. Including lean proteins in your diet can aid in weight loss, boost metabolism, and enhance satiety.
Healthy Fats: Healthy fats are essential for brain function, hormone production, and cell membrane integrity. They also provide a feeling of fullness, which can help with weight management. Sources of healthy fats include avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon and mackerel. Consuming healthy fats can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and improve cognitive function.
Fruits and Vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are packed with vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and dietary fiber. They help protect against chronic diseases, support digestive health, and promote healthy skin. Aim to eat a variety of colors and types of fruits and vegetables to ensure you get a wide range of nutrients. Examples include leafy greens, berries, citrus fruits, carrots, broccoli, and bell peppers.
Limiting Processed Foods, Sugars, and Excessive Salt
Processed Foods: Processed foods often contain added sugars, unhealthy fats, and excessive sodium. They lack essential nutrients and can contribute to weight gain, inflammation, and chronic diseases. Limiting processed foods and opting for whole, minimally processed options can improve overall health.
Sugars: Added sugars provide empty calories and can lead to weight gain, tooth decay, and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. Reducing added sugars in your diet can help manage blood sugar levels and improve overall health. Opt for natural sweeteners like honey, maple syrup, or fruit when possible.
Excessive Salt: High sodium intake can increase blood pressure and contribute to heart disease. Limiting salt intake to less than 2,300 milligrams per day can help maintain healthy blood pressure levels. Choose low-sodium versions of canned and packaged foods, and season your meals with herbs and spices instead of salt.
Mindful Eating, Meal Planning, and Variety in Diet
Mindful Eating: Mindful eating involves paying attention to your hunger and fullness cues, savoring each bite, and eating without distractions. This practice can help you develop a healthier relationship with food, improve digestion, and prevent overeating. Try to eat slowly, chew thoroughly, and focus on the flavors and textures of your food.
Meal Planning: Planning your meals ahead of time can help you make healthier choices and avoid impulse purchases. Consider preparing meals in bulk and storing them in portions for easy access throughout the week. This can save time and money while ensuring you have nutritious options available.
Variety in Diet: Incorporating a variety of foods into your diet ensures you get a wide range of nutrients. Experiment with different cuisines, try new recipes, and explore seasonal produce. This approach can keep your meals interesting and enjoyable while promoting overall health.
Long-Term Benefits of Adhering to These Guidelines
Adhering to these guidelines can have numerous long-term benefits for your overall health and longevity. A healthy diet can reduce the risk of chronic diseases, improve mental health, enhance physical performance, and promote healthy aging. By making informed choices about what you eat, you can enjoy a higher quality of life and a longer lifespan.