Optimizing Performance: Essential Sports Science and Precautions
The field of sports science has revolutionized the way athletes prepare for competition, significantly enhancing both their physical capabilities and mental resilience. By integrating cutting-edge research and practical application, sports scientists can tailor programs that optimize performance while minimizing the risk of injury. This article delves into the core principles of sports science, focusing on nutrition, training techniques, recovery methods, and mental preparation, all crucial elements in achieving peak athletic performance.
Nutrition: The Fuel for Athletic Success
Athletic performance heavily relies on adequate nutrition, which provides the energy and nutrients necessary for optimal functioning. A well-balanced diet supports muscle growth, enhances endurance, and accelerates recovery.
Hydration
Proper hydration is fundamental to maintaining performance levels during exercise. Dehydration can lead to reduced stamina, impaired cognitive function, and increased risk of heat-related illnesses. Athletes should aim to drink fluids before, during, and after workouts, adjusting intake based on activity intensity and environmental conditions.
Balanced Diets
A balanced diet rich in carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats ensures sustained energy levels and supports muscle repair and growth. Carbohydrates serve as the primary fuel source for high-intensity activities, whereas proteins are essential for muscle repair and growth. Healthy fats contribute to overall health and provide long-lasting energy.
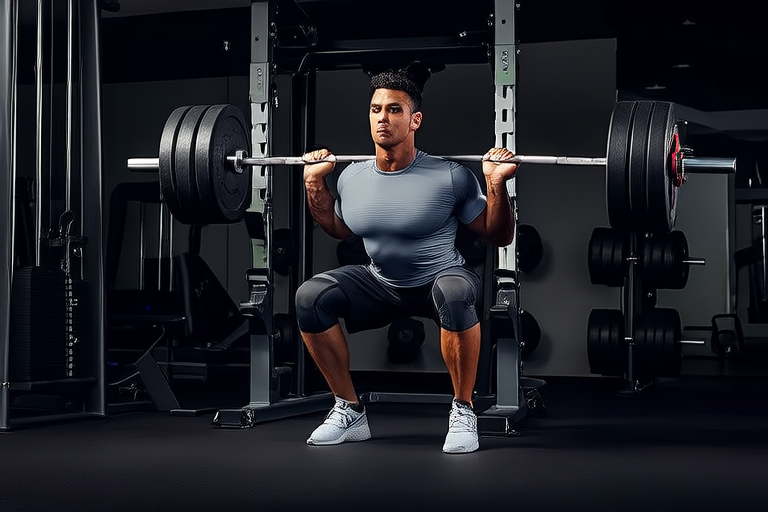
Training Techniques: Building Strength and Endurance
Effective training programs are designed to improve specific aspects of athletic performance, such as strength, speed, and endurance. These programs must be tailored to individual needs and goals.
Strength Training
Strength training involves resistance exercises aimed at increasing muscle mass and improving muscular strength. It is crucial for athletes who need power and explosive movements in their sport. Programs should include compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses, along with isolation exercises targeting smaller muscle groups.
Cardiovascular Exercises
Cardiovascular training improves heart health and lung capacity, essential for endurance events. Regular aerobic exercises such as running, cycling, and swimming enhance oxygen delivery to muscles, thereby increasing endurance and reducing fatigue.
Flexibility Routines
Flexibility routines, including yoga and dynamic stretching, promote joint mobility and reduce the risk of injury. They also improve posture and balance, contributing to overall athletic performance.
Recovery Methods: Ensuring Long-term Health and Performance
Recovery is a critical component of any training regimen. Proper recovery allows the body to adapt to stress, repair tissues, and replenish energy stores.
Proper Sleep Patterns
Sufficient sleep is vital for physical recovery and mental well-being. During sleep, the body releases hormones that aid in muscle repair and growth. Athletes should aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night, prioritizing rest on non-training days.
Stress Management
Mental stress can negatively impact athletic performance by affecting concentration, decision-making, and emotional stability. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and visualization can help manage stress effectively.
Mental Preparation: The Mind-Body Connection
Mental preparation is as important as physical training. Mental toughness, focus, and resilience are key factors in overcoming challenges and achieving success.
Visualization
Visualization involves mentally rehearsing specific skills or scenarios to enhance performance. This technique helps athletes develop confidence and refine their strategies before actual competition.
Goal Setting
Setting realistic and achievable goals motivates athletes to push their limits. Goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Common Injuries and Preventive Measures
Despite careful planning, injuries can occur. Understanding common injuries and taking preventive measures is essential for maintaining health and performance.
Preventive Measures
Warm-up and cool-down routines, proper equipment, and adherence to training guidelines are vital in preventing injuries. Additionally, listening to one’s body and avoiding overtraining are crucial.
Continuous Education and Adaptation
The field of sports science is constantly evolving, with new research and technologies emerging regularly. Athletes and coaches should stay informed about these developments to continuously improve performance.
In conclusion, optimizing athletic performance requires a multifaceted approach that integrates various aspects of sports science. By focusing on nutrition, training techniques, recovery methods, and mental preparation, athletes can achieve their full potential while minimizing the risk of injury. Continuous education and adaptation are key to staying ahead in this ever-evolving field.