Empower Your Body: Essential Guidelines for a Healthy Diet
The journey towards optimal health starts with nourishing your body with the right nutrients. A healthy diet plays a pivotal role in enhancing your overall well-being, boosting energy levels, and supporting mental clarity. It can also help prevent chronic diseases and maintain a healthy weight. Understanding what constitutes a balanced diet and how to implement it into your lifestyle is crucial for longevity and vitality.
Key Components of a Balanced Diet
Macronutrients: The Building Blocks of a Healthy Diet
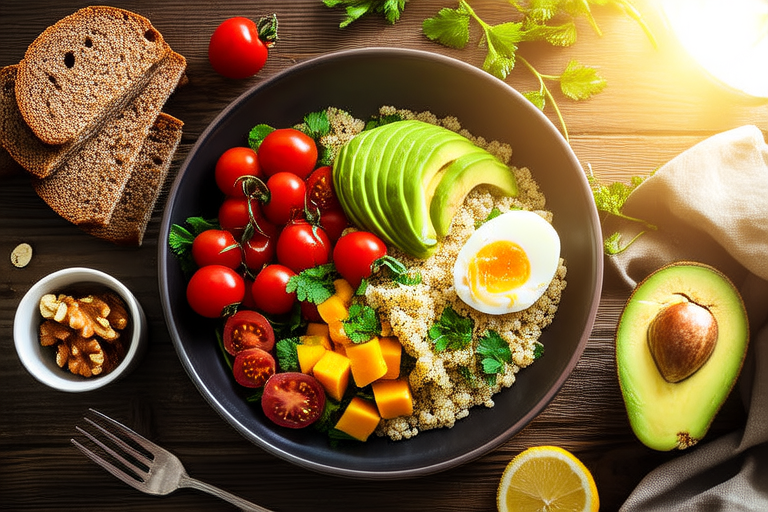
Your diet should include a balance of macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—that provide your body with the necessary fuel to function efficiently.
- Carbohydrates: These are your body’s primary source of energy. Opt for complex carbohydrates like whole grains, vegetables, and fruits which are rich in fiber and take longer to digest compared to simple carbs found in sugary snacks and refined grains.
- Proteins: Proteins are essential for muscle repair and growth. Incorporate lean proteins such as chicken, fish, beans, and lentils into your meals. They also help you feel full longer, aiding in weight management.
- Fats: Not all fats are bad; unsaturated fats, found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, are beneficial for heart health. Limit saturated fats and avoid trans fats altogether.
Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals for Optimal Health
Micronutrients are vital for various bodily functions. They include vitamins and minerals that support immune function, bone health, and metabolism.
- Vitamins: Vitamins play a critical role in maintaining good health. For instance, vitamin C helps in the production of collagen, while vitamin D aids in calcium absorption.
- Minerals: Minerals like iron, calcium, magnesium, and zinc are crucial for different physiological processes. Iron is important for blood oxygenation, calcium supports bone health, and magnesium is involved in muscle and nerve function.
Portion Control and Hydration
Understanding appropriate portion sizes is essential to avoid overeating and maintain a healthy weight. Use smaller plates and bowls to help manage portions, and listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues.
Hydration is equally important. Water is essential for digestion, circulation, temperature regulation, and waste removal. Aim for at least eight glasses of water daily, adjusting based on activity level and climate. Herbal teas, soups, and fruits with high water content can contribute to your fluid intake.
Whole Foods vs Processed Foods
Whole foods are minimally processed and retain their natural nutrients. Examples include fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and dairy products. They offer more nutritional value and fewer additives than processed foods.
Processed foods often contain added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium. While they may be convenient, they lack the essential nutrients needed for good health. Gradually incorporating more whole foods into your diet can lead to better health outcomes.
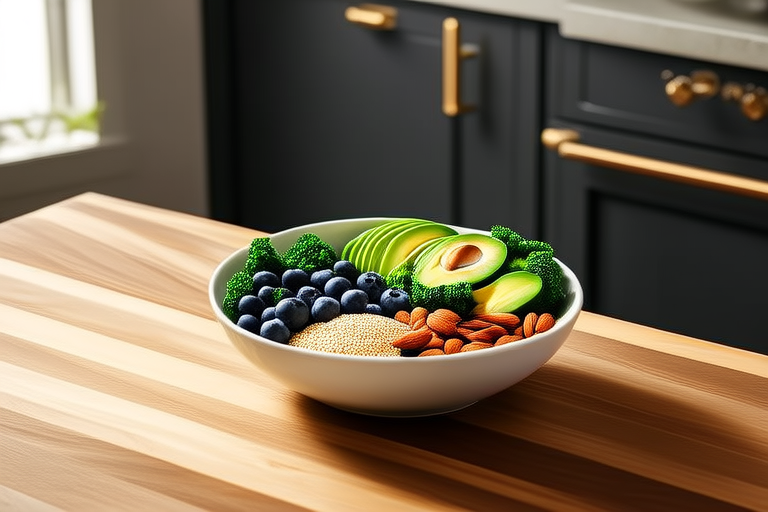
Fiber, Healthy Fats, and Lean Proteins
Incorporating fiber-rich foods like legumes, whole grains, and vegetables can improve digestion and help regulate blood sugar levels. Fiber also adds bulk to meals, promoting satiety and aiding in weight management.
Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, fatty fish, and nuts, are beneficial for heart health. They can reduce inflammation and lower cholesterol levels when consumed in moderation.
Lean proteins are crucial for muscle maintenance and repair. They also help in regulating appetite and metabolism. Opt for sources like skinless poultry, fish, tofu, and legumes to ensure a healthy intake of protein.
Tips for Meal Planning, Grocery Shopping, and Cooking Techniques
Meal planning can help you stay on track with your dietary goals. Prepare a weekly menu and make a shopping list to avoid impulse buys. When grocery shopping, choose fresh produce, lean proteins, and whole grains over processed options.
Simple cooking techniques like steaming, grilling, and baking preserve nutrients better than frying. Experiment with herbs and spices to add flavor without relying on salt or unhealthy fats. Preparing meals in advance can save time and ensure you have healthy options available throughout the week.
Listening to Your Body and Sustainable Dietary Habits
It’s important to listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues. Eating mindfully allows you to recognize when you’re truly hungry and when you’ve had enough. This practice can help prevent overeating and promote a healthier relationship with food.
Sustainable dietary habits are key to long-term health. Avoid fad diets that promise quick results but are difficult to maintain. Instead, focus on making gradual changes that you can incorporate into your lifestyle for lasting benefits.
By following these guidelines and staying committed to your health, you can empower your body and enhance your overall well-being. Remember, small, consistent changes can lead to significant improvements in your health and quality of life.