Maximizing Performance: Sports Science Insights and Essential Precautions
1. Introduction to Key Principles of Sports Science that Enhance Athletic Performance
Sports science encompasses a broad spectrum of disciplines aimed at understanding and enhancing athletic performance. At its core, it integrates biomechanics, physiology, psychology, and nutrition to provide athletes with actionable insights. One fundamental principle is the concept of specificity, which posits that training should closely mimic the demands of the sport. This ensures that the body adapts specifically to the movements and stresses encountered during competition.
Another critical aspect is periodization, a structured approach to training that involves cycling through phases of varying intensity and volume. Periodization helps prevent overtraining, enhances recovery, and promotes sustained improvements in performance. Additionally, the principle of overload suggests that to achieve gains, athletes must progressively increase the demands placed on their bodies beyond what they have previously experienced. This incremental challenge drives adaptation and improvement.
Psychological aspects also play a pivotal role. Mental preparation techniques, such as visualization and mindfulness, can significantly impact an athlete’s ability to perform under pressure. These practices help manage stress, improve focus, and boost confidence. Understanding these principles equips athletes with a comprehensive framework to optimize their training and compete at their peak.
2. Detailed Exploration of Evidence-Based Training Techniques Supported by Sports Science
Effective training programs are grounded in evidence-based methodologies derived from sports science research. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) has emerged as a highly efficient method for improving cardiovascular fitness and increasing anaerobic capacity. HIIT involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief recovery periods, leading to significant metabolic adaptations.
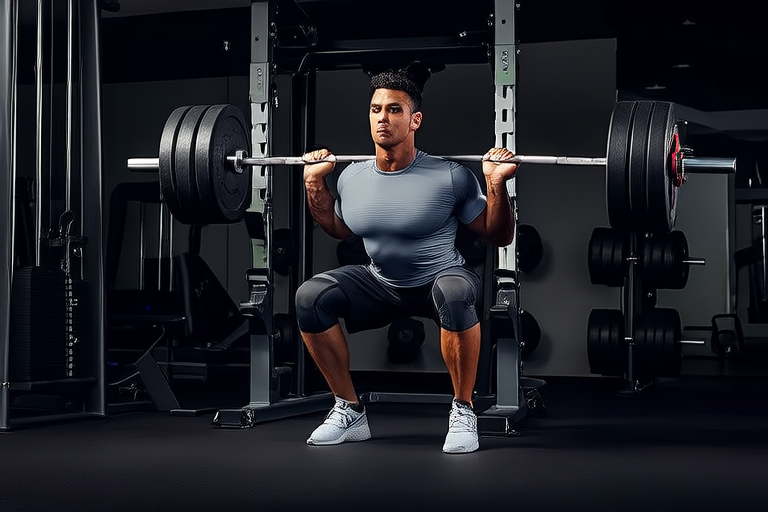
Resistance training is another cornerstone of performance enhancement. Incorporating compound exercises that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, like squats and deadlifts, maximizes strength gains and functional movement efficiency. Progressive overload, where weights are gradually increased, ensures continuous progress. Additionally, incorporating plyometric exercises can enhance power and explosiveness, crucial for many sports.
Flexibility and mobility training are often overlooked but are vital for preventing injuries and maintaining optimal performance. Stretching routines should be dynamic, focusing on full range of motion and joint health. Yoga and Pilates are beneficial for improving flexibility, balance, and core strength, all of which contribute to better overall athleticism.
Recovery is equally important as training itself. Active recovery, such as light jogging or swimming, can aid in muscle repair and reduce soreness. Cryotherapy, contrast water therapy, and massage are other modalities shown to accelerate recovery times. By integrating these techniques, athletes can maintain high levels of performance throughout their competitive seasons.
3. Explanation of Nutritional Strategies Crucial for Optimal Performance and Recovery
Nutrition plays a critical role in fueling workouts, supporting recovery, and optimizing body composition. A balanced diet rich in carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats provides the necessary energy and building blocks for muscle repair and growth. Carbohydrates are particularly important for endurance athletes, serving as the primary source of energy during prolonged physical activity.
Protein intake is essential for repairing and building muscle tissue. Athletes should aim for approximately 1.2 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily, depending on their specific needs and goals. Consuming protein within 30 minutes post-exercise can enhance recovery and promote muscle synthesis. Quality sources include lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, and plant-based alternatives.
Hydration is often underestimated but is crucial for maintaining performance and preventing heat-related illnesses. Athletes should drink fluids before, during, and after workouts, aiming to replace fluids lost through sweat. Electrolyte replenishment is also important, especially in hot conditions or during prolonged exercise. Sports drinks containing sodium, potassium, and magnesium can help maintain fluid balance and support nerve and muscle function.
Supplements can complement a well-balanced diet but should not replace whole foods. Creatine, beta-alanine, and caffeine are popular among athletes due to their potential benefits in enhancing strength, endurance, and mental acuity. However, individual responses vary, so it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
4. Discussion on Injury Prevention Methods and the Importance of Proper Precautions
Injury prevention is paramount for maintaining long-term athletic success. Proper warm-up and cool-down routines are foundational. A dynamic warm-up prepares muscles and joints for activity, increasing blood flow and reducing stiffness. Cooling down with static stretching helps relax muscles and improves flexibility.
Strength training for weak areas can address imbalances and reduce the risk of injury. For instance, strengthening the glutes and core can protect the lower back and knees. Balance and proprioception exercises, such as single-leg stands and agility drills, improve stability and coordination, further safeguarding against falls and sprains.
Appropriate equipment and footwear tailored to the specific demands of one’s sport are essential. Shoes should provide adequate support and cushioning, while protective gear, like helmets and pads, should fit properly and meet safety standards. Regular maintenance and replacement of worn-out gear are also important.
Lastly, listening to one’s body and recognizing signs of overuse or fatigue is crucial. Ignoring persistent pain or discomfort can lead to more severe injuries. Rest days are just as important as training days; they allow the body time to recover and adapt. Athletes should also incorporate regular medical check-ups and seek professional advice when needed.